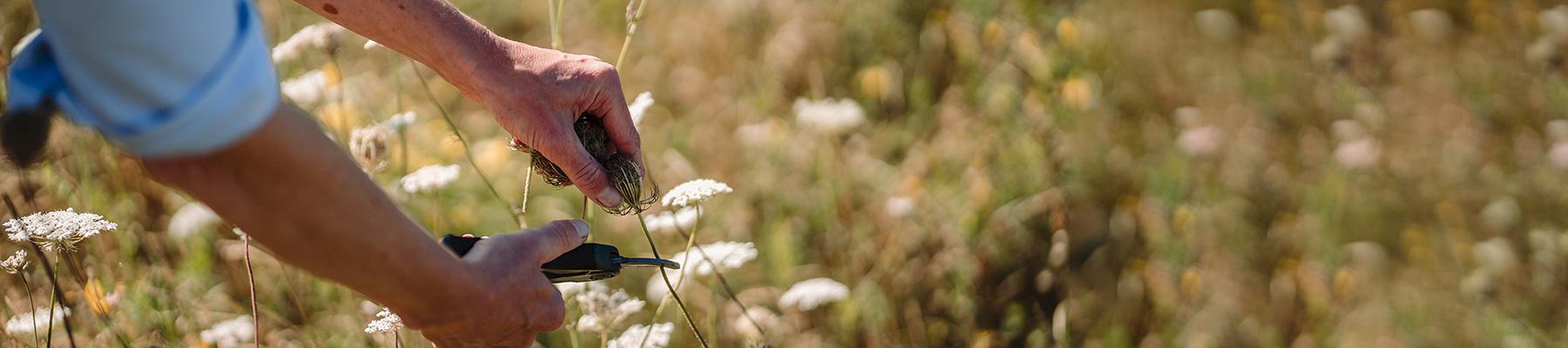
photo: Sally Gouldstone
i
Enhancing landscape restoration with sustainable use
With one in five people worldwide depending on wild plants, algae, and fungi for food and income, integrating the sustainable use of wild species into landscape restoration is not just beneficial—it can be essential.
By aligning restoration efforts with the needs of local communities, restoration practitioners can protect biodiversity while ensuring that ecosystems continue to provide critical resources. This approach helps shift practices away from overexploitation, which often drives degradation, and instead fosters long-term ecological resilience.
1 in 5 people
rely on wild plants, algae and fungi for their food and income
How our guidance can help
Our guidance equips restoration professionals with practical tools and real-world case studies from Europe and Africa, demonstrating how sustainable wild species use can enhance restoration outcomes. By enabling communities to benefit economically from restored landscapes, this strategy can build local support, strengthen project impact, and promote a more inclusive, sustainable future for both people and nature.
RESTORATION PRACTITIONER TOOLKIT
Determine if integrating the sustainable use of wild species can support your project goals
Identify which wild native plants and fungi are most suitable for sustainable harvest and trade
Develop sustainable harvest management plans
ONLINE COURSE
All you need to know about enabling sustainable use of wild species in landscape restoration projects.

PRACTITIONER GUIDANCE
Our complete guidance, which can be downloaded for use offline.

PROJECT WEBINAR
Enhancing landscape restoration with nature-positive economies through sustainable use of wild plants and fungi
ASSOCIATED RESOURCES AND TEMPLATES
Example project risk assessment
A completed template that demonstrates a comprehensive project risk assessment.
ISSC Guidance
Implementing the International Standard for Sustainable Wild Collection of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (ISSC-MAP) 2008 and 2010.
Decision tool template
A template for completing a situational analysis with stakeholder consultations.
Risk assessment
A template for categorising and ranking risks and mitigation strategies.
Species use assessment
A template for analysing species, commodity, and intrinsic contextual factors.
CASE STUDIES

ROMANIA
Creating alternative income sources in landscapes where logging contributes to environmental degradation

SCOTLAND
Combining ecological management with socio-economic goals in the Scottish Cairngorms

SPAIN
Supporting improved socio-economic opportunities in a landscape affected by rural abandonment in Spain

SCOTLAND
Planting species with commercial value as well as ecological benefits to fund further restoration in Scotland

KENYA
Training and capacity building to address unsustainable harvesting methods where this has contributed to degradation

MALAWI
Enabling alternative livelihoods opportunities where conversion of land to farmland is a driver of degradation

SUDAN
Implementing the replanting of wild native species with a history of use to revive traditional livelihoods in Sudan
donors and partners
The guidance was developed by TRAFFIC in collaboration with the IUCN SSC/CEESP Sustainable Use and Livelihoods Specialist Group, the FairWild Foundation, and The Global Biodiversity Standard.
The development of this guidance was funded by the Endangered Landscapes & Seascapes Programme and the UK Government Darwin Initiative project DAREX001 for Developing a Global Biodiversity Standard certification for tree-planting and restoration.
Endangered Landscapes and Seascapes Programme (ELSP)
The Endangered Landscapes & Seascapes Programme aims to restore natural ecological processes, species populations and habitats for a better and more sustainable future. It signals a shift away from a narrative of ‘slowing declines’ and ‘no net loss’ to a positive and creative conservation agenda in which the potential of our land and seas is recognised. The Endangered Landscapes & Seascapes Programme is managed by the Cambridge Conservation Initiative in partnership with Arcadia, a charitable foundation that works to protect nature, preserve cultural heritage, and promote open access to knowledge.